free5GRAN architecture is split into two parts. The first part is the library which contains common functions and the second part is the implementation which contains custom code for the transmitter and the receiver. free5GRAN code and documentation are available online (https://github.com/free5G/free5GRAN). The following figure represents free5GRAN architecture:
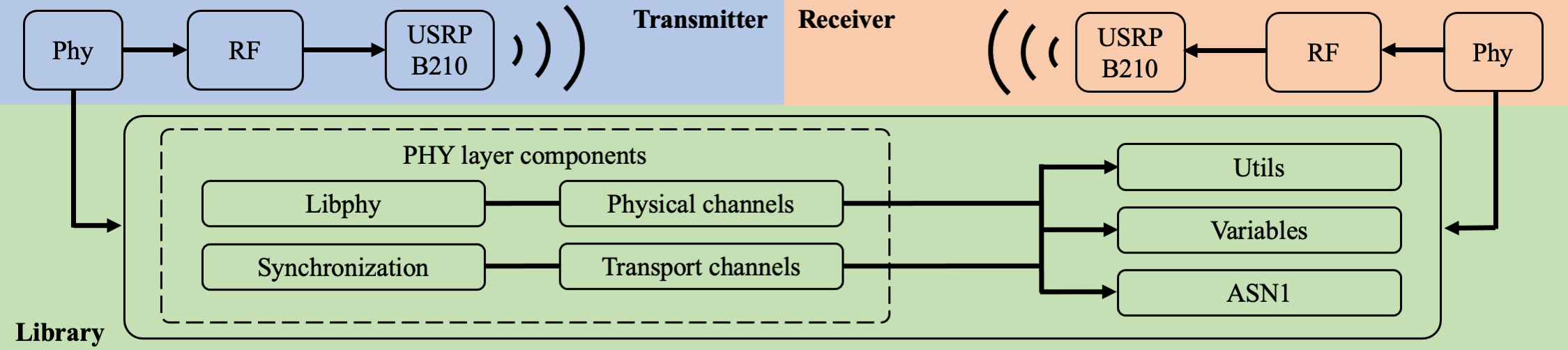
Library
The library is a set of static functions and variables that might be commonly used by both receiver and transmitter, or even by other similar projects. All the functions have been designed to be used independently. It is split into four parts, which are phy, utils, variables and asn1c.
phy
The phy library contains the code for PHY layer processing. It is split into four parts which represent different 5G RAN stack components. Those parts are libphy for signal processing functions, physical_channel for physical channels processing, transport_channel for transport channels processing and synchronization for time and frequency synchronization procedures. Main functions of the different libraries, that will be depicted later, are:
libphy: channel estimation, demodulation and channel mapping/de-mapping.physical_channel: PBCH, PDCCH and PDSCH decoding, defined in TS 38.211 Section 7.3.transport_channel: Broadcast Channel (BCH), Downlink Control Information (DCI) and Downlink Shared Channel (DL-SCH) decoding, and all related sub-functions, defined in TS 38.212 Section 7.synchronization: Primary and Secondary Synchronization Signals (PSS and SSS) correlation for time synchronization.
utils
It contains functions that are called at different levels of the code. Main functions are:
- Scrambling: takes an input bits sequence (hard or soft bits) and scramble it with another bits sequence. This is used for both physical and transport channel;
- Synchronization sequences generation: generates PSS and SSS sequences for receiver time synchronization, as defined in TS 38.211 Section 7.4.2.
- PBCH, PDCCH and PDSCH DMRS sequences generation: generates pilot sequences for channel estimation, as defined in TS 38.211 Section 7.4.1.
- Pseudo random sequence generation: generates a pseudo random sequence based on an initialization value
cinit, as described in TS 38.211 Section 5.2.
variables
It is a set of variables and data structures definitions used by both the library and implementation. Most important variables are:
- Global variables defined in the standard.
- Polar coding matrices:
Gnmatrices,n in [5,10], for polar coding (defined in TS 38.212 Section 5.3.1.2) and corresponding inverse matrices for polar decoding. - LDPC base graphs, defined in TS 38.212 Section 5.3.2.
asn1c
It contains the code and structures for encoding and decoding RRC messages. It uses the ASN1C library. In the current implementation, it is used by the receiver to decode SIB1 data. The library is currently able to parse and encode all the RRC PDU messages and types defined in TS 38.331 Section 6.2.
Implementation
The implementation part provides code dedicated for the receiver. It is built using objects that store different processing information and exposes method for receiver functionalities implementation. It is split in two main classes that are rf and phy.
rf
This class represents the RF device. It stores information about RF device configuration and current state and exposes method for receiving and transmitting signal from it. Future releases will include an interface at this level so that many different RF devices can be supported. In the current version, free5GRAN supports USRP B210 and uses USRP UHD library [libuhd]} for device exchanges.
phy
This class represents the receiver phy layer. It stores different cell and PHY layer status information. It exposes methods for cell synchronization, physical channel extraction and data decoding.
